Simulation#
MD Simulation and how to post process the results#
MD simulations are used to simulate the movement of RNA and dyes, essential for simulating smFRET experiments and generating FRET distributions [6]. For these simulations, GROMACS [7] serves as the program, requiring installation and compilation of the software.
Within the developed pipeline, force field and parameter files are provided for the simulations. To initiate an MD simulation, several parameters need to be defined (Parameter: MD simulation), including simulation time, temperature, magnesium ion concentration, and the distance from the structure to the simulation box’s edge. After specifying a MD results directory, the necessary files are copied to the folder, and the simulation starts. The required GROMACS commands are executed sequentially to solvate the molecule and launch the MD run.
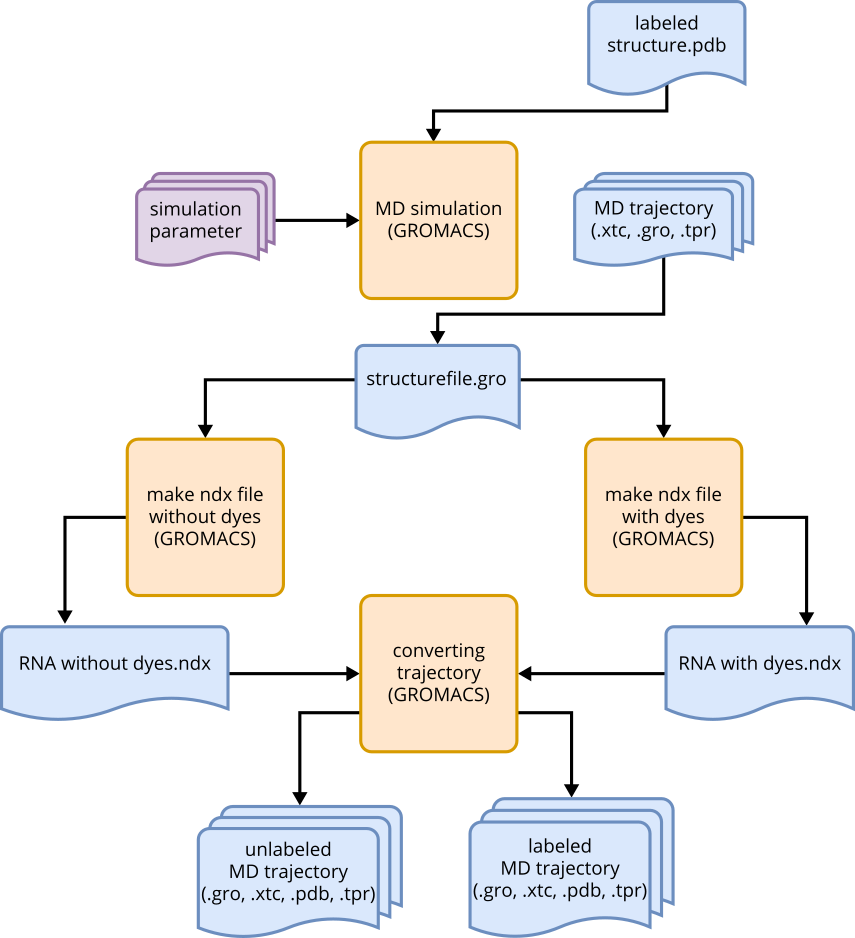
Fig. 7 Workflow for performing MD simulations and subsequent data processing.#
Solvation#
The following steps are done to solve the molecule:
Using
pdb2gmx, the PDB format is converted to a GROMACS preferred .gro format and a topology file is generated. The force field provided by the pipeline is automatically selected. Here, errors may occur if atom or residue names in the PDB file cannot be assigned to the atom or residue names in the force field.The simulation box is defined using
editconf, with the dist_to_box parameter. Here, the molecule’s size determining the box’s dimensions.The molecule is placed in the box and solvated with water using the
solvatemodule. The TIP4P water model with Ewald optimization is automatically chosen.Ions are added randomly to the system, replacing water molecules. For monovalent metal ions potassium ions are added until the system is neutralized, considering the negatively charged backbone of the RNA. The concentration of divalent metal ions, Mg2+ in this case, is defined by the parameters. These concentrations can match the experiment, but due to the small size of the simulation box, the number of added ions can be artificial.
The simulation is performed using
mdrun, which carries out energy minimization to correctly arrange the water molecules. The atoms of the RNA are positionally restrained during this step.
MD run#
To run a simulation, the following steps are performed:
Following energy minimization, a temperature and pressure equilibrium should be established. Parameter files, known as mdp files, are created for temperature and pressure equilibration. These files contain the necessary settings for these equilibration steps.
The mdp files are read and a run input file is generated using the
gromppmodule. This input file incorporates all the instructions required for the simulation.For temperature equilibration, a dedicated directory named nvt is created to store the simulation results. A simulation run using mdrun is executed for a duration of 300 ns to allow the system to reach the desired temperature equilibrium.
Similarly, a directory named npt is generated to store the results obtained during pressure equilibration. Another simulation run using mdrun is performed to achieve pressure equilibrium in the system.
The MD long run is configured to obtain an extended simulation. The desired simulation time in nanoseconds (ns) is specified using the parameter setting simulation_time[ns]. The file md0.mdp is adjusted accordingly to set the desired simulation time.
A run input file is generated using
gromppbased on the updated configuration. This input file includes all the necessary information for executing the MD run.The MD run is executed using
mdrunto obtain full simulation results. The results from the MD run are saved in the designated directory named md0.
After MD simulations a trajectory including an xtc, gro, and tpr file are available for further processing. The xtc files contain compressed information about the trajectory, while the gro files provide details about the structure of the simulated molecule. The tpr file contains the topology information.
In the first step of the MD analysis, the MD trajectory is reduced to atoms related to the RNA molecule. Additionally, the dyes are also removed, resulting in two trajectories: one with explicit dyes and one without dyes. This step is necessary when generating an ACV trajectory from a simulation with explicit dyes. To reduce simulation files, index files (ndx) are required. These files list atom numbers that should be retained during trajectory conversion.
The functions make_ndx_of_rna() and make_ndx_of_rna_without_dyes() are used for this purpose. The second
function lists only the atoms found in the RNA, excluding the dyes. Using the GROMACS module trjconv,
xtc files can be converted and pdb files can be created, using the ndx files. This process resolves the
periodic boundary conditions and places the molecule in the center of the box. Ultimately, two trajectories
are obtained, one for the RNA without water molecules and ions, and an additional one without dyes.
Both trajectories include a reduced xtc file, a tpr file, a reduced gro file, and a PDB file of the initial
state of the trajectory.